
Vitality curve is a concept in which the employees of an organization are graded based on their individual productivity. It is also called as rank and yank, forced distribution, stack ranking, stack ranking andforced ranking. It is based on the Pareto principle. This method is used about 60% of US Fortune 500 corporations. But some companies have stopped using this method due to the criticism that it has drawn.
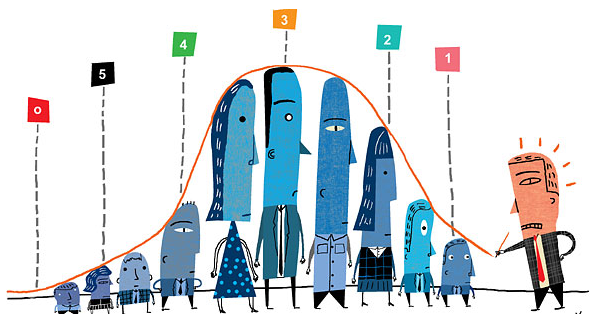
The vitality model that was developed by Jack Welch has been described as a “20-70-10” system. It says that top 20% of the workforce is most effective. The next 70% work at a satisfactory level followed by bottom 10% who are not at all productive and should be fired. The organizations in which this system implemented, have shown an increase in revenues and earnings.
Welch says that top executives should be divided into “A”, “B” and “C” players. The characteristics of these players are as follows:
“A” Players
- Full of passion
- Believe in completing tasks
- Open to ideas
- Have charisma
- Can make business productive as well as enjoyable
- Exhibit high energy levels
“B” Players
These are the people who work at a satisfactory level. As they are majority of the workforce, they are important for the organization even though they might not depict the skillset of “A” players.
“C” Players
These are the non-productive players. They show procrastination and very often fail to fulfil their promises. They slow down the rate of progress of the organization.
Advantages
- Under this system managers are forced to rate the employees which would otherwise would not have been possible If such a system was not in place.
- The organization is able to recognize its worst performers and thus take appropriate actions to improve the overall performance of the organization.
- It has allowed HR’s to be completely transparent about compensation.
Disadvantages
- According to Welsh, ”A” players should be rewarded and promoted in the organization while the “C” players should be fired. However it must be noted that when an “A” player is promoted, he will be a top performer at the current job level. But when promoted, he may keep on working on the same level. This level may not meet the expectations and hence the employee may become “B” player. If the compensation received for “B” player at the higher level is lower than that received by “A” player at a lower level, it may result in reduction in overall compensation of the employee and ultimately refusal of promotion.
- When employees are involved in hiring their peers, they may prefer to avoid the best candidates with the fear that if the best candidates are selected, they may face more competition at the “A” end of the curve. It would thus lead to the hired people to fit into the “C” category.
Companies using this philosophy
Management consulting
Management consulting firms, including the Big Four generally have this system. Specifically in PricewaterhouseCoopers and Accenture, an approach is used where if an employee is not promoted after a certain length of time, then the employee is fired from the organization but on generous terms. The employees of Accenture are rated based on their performance twice a year.
GE
GE was the first and the most famous organization to implement this system. However after the departure of Jack Welch from the organization, the system has become less important and focus is places to improve the bottom placed players.
Enron
Enron showcased the cons of using this system. The employees of Enron, with the fear of being fired, inflated the results and this ultimately lead to the downfall of the organization.
Motorola
Motorola implemented the plan named IDE (Individual Dignity Entitlement) in mid-90’s which was similar to vitality curve. The name of the plan was changes to PM (Performance Management). This lead to about 50000 employees of Motorola, globally, losing their jobs.
Dow Chemical
Curve program is used by Dow Chemical as part of its Performance Management. The program was started in 2005 and has been delivering mixed results.
IBM
IBM uses a vitality curve program known as Personal Business Commitments (PBC). The PBC process involves managers have to give a limited number of favorable rankings to the employees. An employee’s rating is not only dependent on manager’s opinion, but also on opinion of the 2nd line manager on 1st line manager.
Yahoo
QPR (Quarterly Performance Review) system was institutes in Yahoo by CEO Marissa Mayer in 2012. This system, just like vitality curve divided employees under various categories.
References
Economist – Ranked and Yanked, Strategy Business – The Folly of Forced Ranking, Rediff Business – The Rank and Yank Appraisal System


